The Definition of Marketing Qualified Leads, Sales Qualified Leads, and Sales Accepted Leads
Definition of Prospects, Marketing Qualified Leads (MQL), Sales Qualified Leads (SQL), Sales Accepted Leads (SAL)
Understanding the different stages of leads is crucial for optimising your sales funnel. In this article, we will explore the definitions of Prospects, Marketing Qualified Leads (MQL), Sales Qualified Leads (SQL), and Sales Accepted Leads (SAL). We’ll dive into their characteristics, importance, and how they transition from one stage to another.
What are Prospects?
Introduction to Prospects: Prospects are potential leads who may not know your company yet but fit within your target audience. They can be identified through various public databases. Imagine a typical Yellow Pages directory or telephone book directory.
Characteristics of Prospects: Prospects typically have basic demographic information available, such as name, company, and contact details.
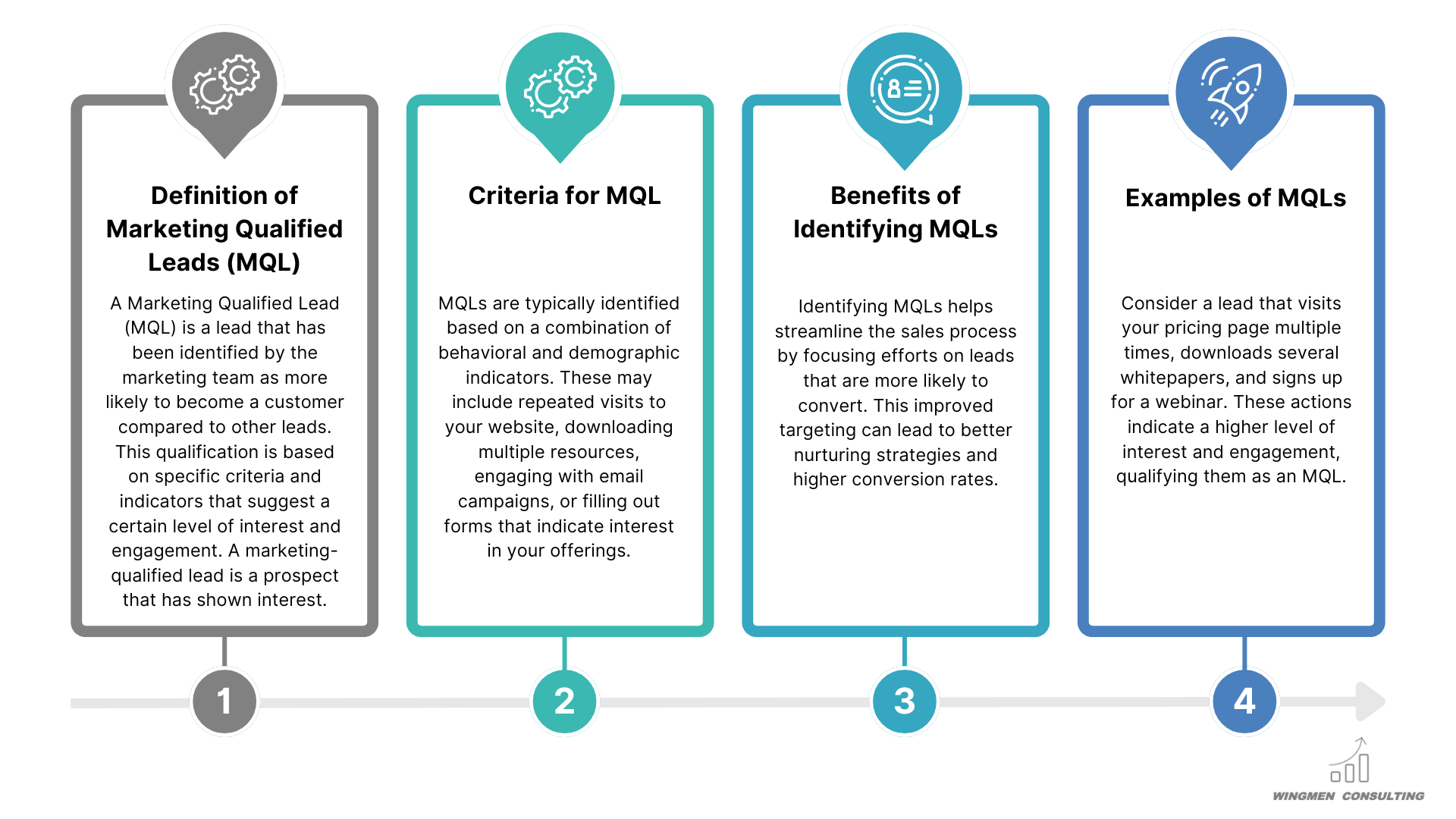
What are Marketing Qualified Leads (MQL)?
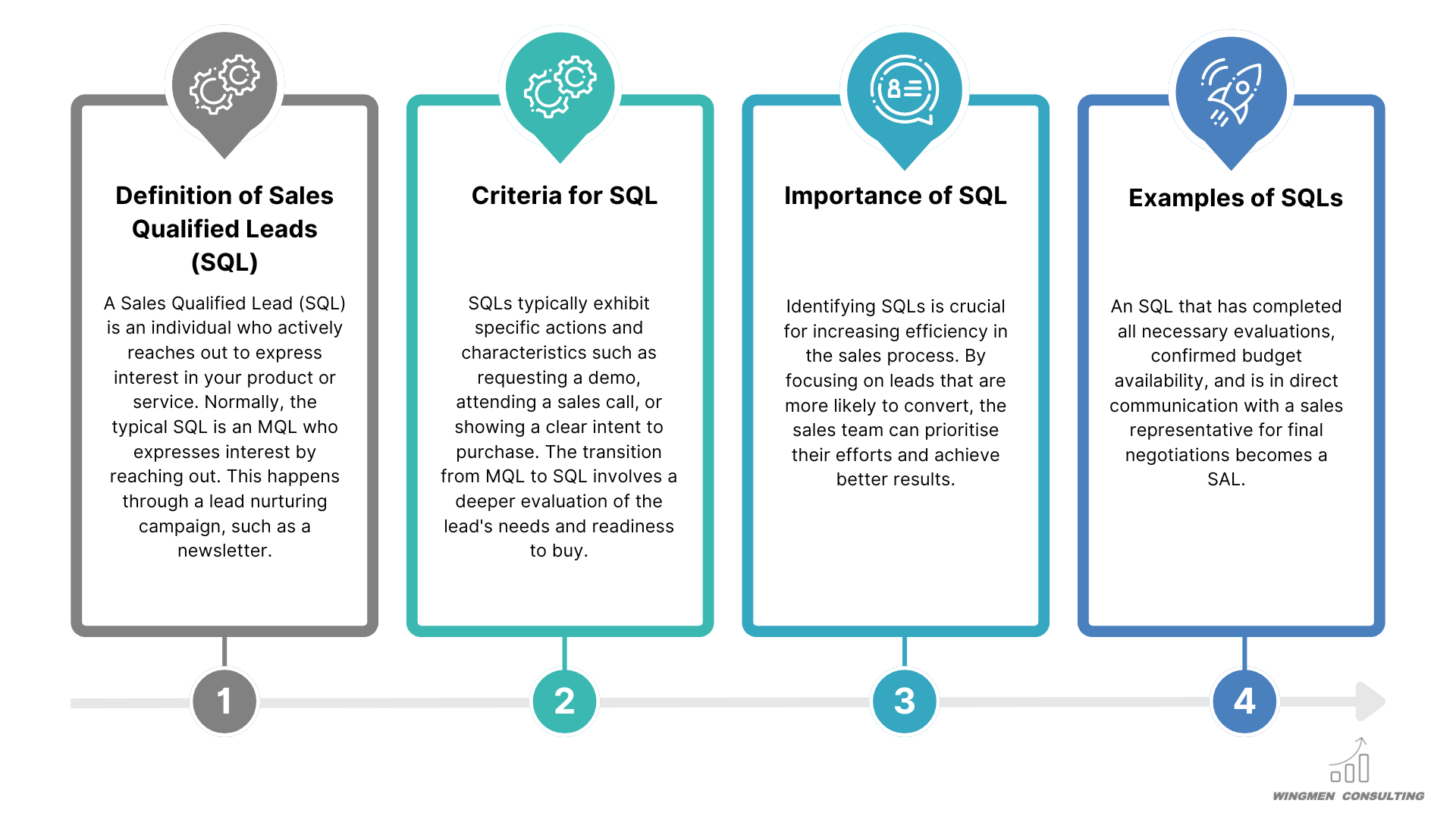
What are Sales Qualified Leads (SQL)?
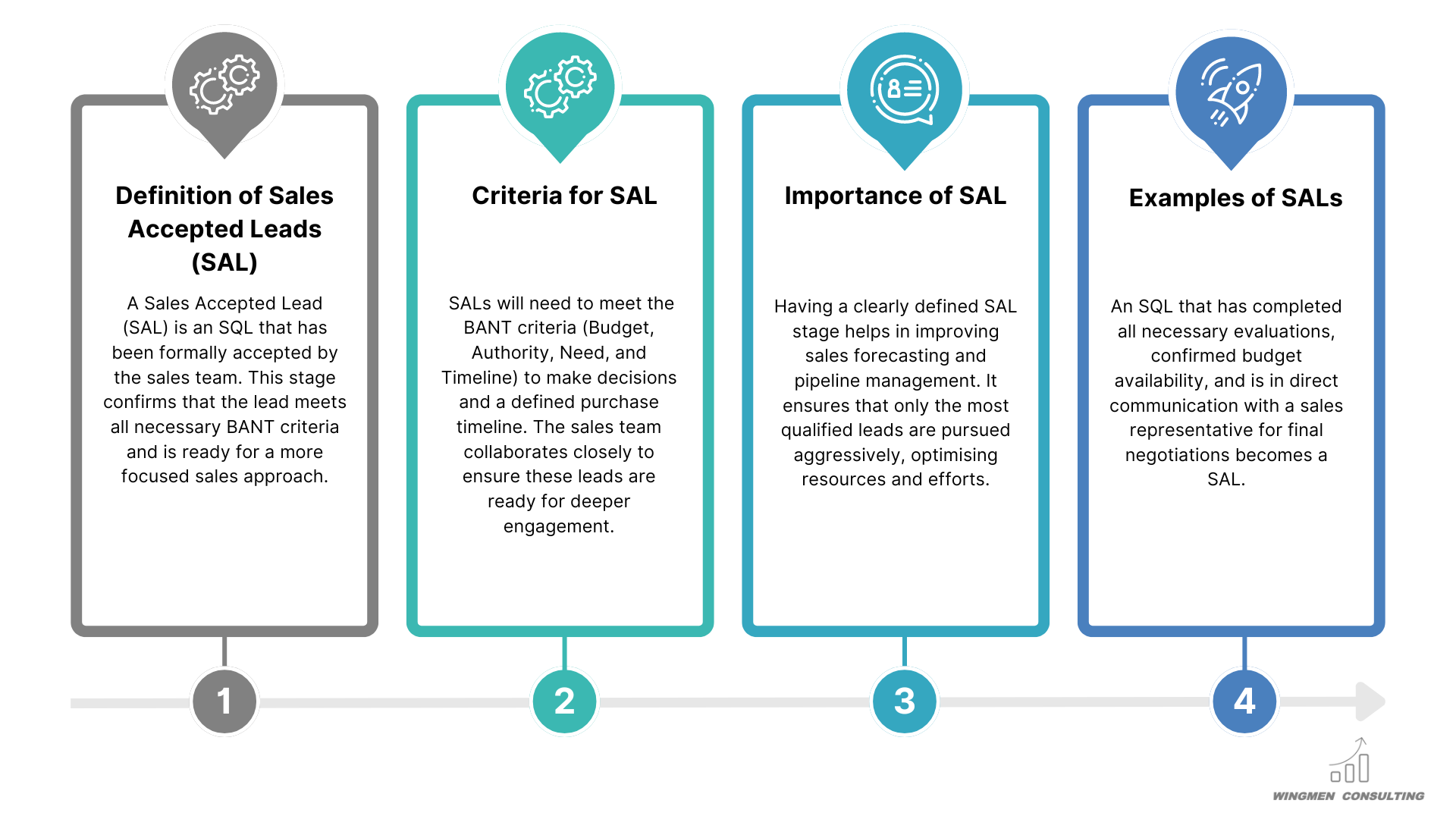
What are Sales Accepted Leads (SAL)?
How to Qualify a Marketing Qualified Lead to a Sales Qualified Lead?
Process of Qualification
The transition from a Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) to a Sales Qualified Lead (SQL) is a critical phase in the lead nurturing process. This journey involves several essential steps to ensure that leads are adequately engaged and assessed for their readiness to enter the sales pipeline.
First, further engagement with the lead is necessary. This means going beyond the initial interaction and providing more personalized content that aligns with the lead’s specific interests and pain points. Engagement can be monitored through various indicators such as email opens, click-through rates, and interactions with targeted content like webinars, whitepapers, and case studies. The depth and frequency of these engagements can provide significant insights into the lead’s level of interest and readiness for a sales conversation.
Second, personalized communication plays a crucial role. This involves tailoring follow-up messages that address the specific needs and behaviors of the lead. Personalized emails, one-on-one meetings, and customized offers can help in nurturing the lead further. The goal here is to create a meaningful dialogue that builds trust and positions your product or service as the ideal solution to their problems.
Lastly, a thorough needs assessment is essential. This step involves a deeper dive into understanding the lead’s challenges, goals, and requirements. Sales teams often use discovery calls or exploratory meetings to gather detailed information. Key indicators of a lead’s readiness to transition to SQL include direct inquiries about pricing, requests for product demonstrations, and engagement with sales materials such as detailed product brochures or ROI calculators.
Best Practices
Effective lead qualification is not a solitary task; it requires close collaboration between marketing and sales teams. This collaboration ensures that both teams are aligned on the criteria for what constitutes an MQL and an SQL, and it helps in creating a seamless transition process.
Regular meetings between marketing and sales are crucial. These meetings provide an opportunity to discuss lead quality, share insights, and refine qualification criteria based on real-world interactions. Clear communication channels must be established to facilitate the quick exchange of information and feedback.
Another best practice is to implement a lead scoring system. This system assigns points to leads based on their behavior and engagement with your marketing efforts. For example, downloading a whitepaper might score more points than just visiting a webpage. This scoring system helps prioritize leads who are more likely to convert and ensures that sales teams focus their efforts on high-potential prospects.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
One of the most common challenges in qualifying leads is the misalignment between marketing and sales teams. This misalignment can result in leads being passed to sales too early or too late, leading to missed opportunities or wasted resources.
To overcome this, it is essential to implement a feedback loop. Sales teams should regularly provide feedback to marketing on the quality of leads received and the outcomes of their interactions. This feedback helps marketing refine their strategies and improve the lead qualification process.
Consistency in criteria is also vital. Both teams must agree on the definition of an MQL and an SQL, ensuring that there is no ambiguity in the qualification process. This consistency can be achieved through documented processes and regular training sessions.
How to Qualify a Sales Qualified Lead to a Sales Accepted Lead?
Process of Qualification
Transitioning an SQL to a Sales Accepted Lead (SAL) involves confirming the lead’s readiness to buy. This step is critical as it moves the lead closer to conversion, ensuring that sales efforts are focused on leads with a high likelihood of closing.
The qualification process typically involves verifying the Budget, Authority, Need, and Timeline (BANT) criteria. This means confirming that the lead has the financial capacity to make a purchase, the authority to make buying decisions, a genuine need for your product or service, and an appropriate timeline for making the purchase.
Direct communication with the lead is essential at this stage. Sales representatives should engage in detailed discussions to gather information about the lead’s budget constraints, decision-making process, specific needs, and expected timeline. This direct interaction helps in building a clearer picture of the lead’s readiness and potential barriers to purchase.
Best Practices
Building strong relationships with leads is paramount during this stage. The sales team should focus on understanding the lead’s specific needs and providing tailored solutions that address these needs. Personalized proposals, detailed product demonstrations, and one-on-one meetings can help in building trust and demonstrating the value of your offering.
Promptly addressing any concerns or objections raised by the lead is also crucial. This proactive approach shows that you value their business and are committed to providing the best possible solution. By being responsive and attentive, you can ease any anxieties the lead might have and move them closer to making a buying decision.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
One of the common challenges in this stage is dealing with leads that stall or change their minds. This can happen for various reasons, including changes in their internal priorities or external market conditions.
Maintaining regular follow-ups is essential to keep the lead engaged. Scheduled check-ins, follow-up emails, and offering additional information or resources can help in keeping the conversation alive. It’s also important to provide continuous value during these interactions, whether through insights, industry reports, or case studies that reinforce the benefits of your solution.
Conclusion
Mastering the journey from prospects to Marketing Qualified Leads (MQL), Sales Qualified Leads (SQL), and Sales Accepted Leads (SAL) can transform your sales process. By understanding these stages and nurturing leads effectively, you can align your marketing and sales teams, streamline your efforts, and ultimately boost your conversion rates. Think of it as building a relationship: starting with a hello (prospects), showing genuine interest (MQL), engaging in meaningful conversations (SQL), and finally, making a commitment (SAL). With this approach, you’ll not only improve your sales pipeline but also create lasting connections with your customers.
